A foot switch, also known as a footswitch or foot pedal, is a device that allows users to control an electrical circuit or mechanical system by pressing their foot. These switches offer hands-free convenience, allowing users to perform tasks more efficiently while keeping their hands free for other activities.
Foot switches are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, music, and robotics, and are a valuable tool for improving productivity, safety, and overall workflow.
Whether you’re a musician, healthcare professional, or factory worker, understanding the types, applications, and benefits of foot switches is crucial to optimizing their use.
Understanding Foot Pedal Switches
Foot pedal switches operate on a simple principle: when you press the pedal, it activates or deactivates a circuit. The switch typically has two states—on or off—and functions based on the pressure applied by the user’s foot. Foot switches are used to control a wide range of devices, from simple household equipment to complex industrial machinery, depending on the application.
These switches are designed to be durable, responsive, and comfortable to operate for extended periods. Modern foot pedal switches often feature ergonomically designed pedals that reduce foot fatigue and offer smooth actuation. They also include safety features such as emergency stop buttons, anti-slip surfaces, and adjustable pressure sensitivity to ensure they meet the specific needs of different industries.
Types of Foot Pedal Switches
There are several types of foot pedal switches, each designed for specific functions and applications. Below are the most common types of foot switches you may encounter:
1. Momentary Foot Switches
Momentary foot switches are the most common type of foot switch. They remain active only as long as the pedal is pressed. Once you release the pedal, the circuit returns to its default state. These switches are typically used for applications that require temporary activation, such as controlling sewing machines, dental equipment, or even lighting systems.
Momentary switches are versatile and ideal for tasks where continuous activation is not required. For example, a musician may use a momentary footswitch to trigger a specific effect, such as turning on a distortion pedal during a guitar solo, while turning it off when not in use.
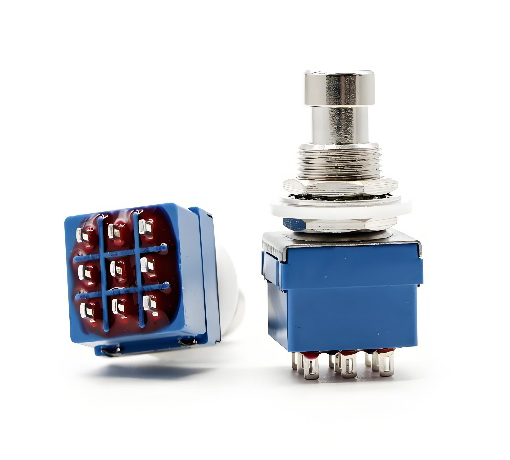
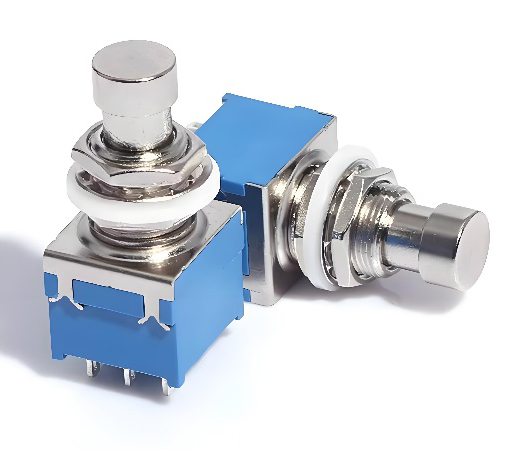


2. Latching Foot Switches
Latching foot switches toggle between two states (on/off) with each press. Pressing the foot pedal once activates the circuit, while pressing it again deactivates the circuit. Latching foot switches are often used in applications where continuous activation is required without holding the pedal down, such as controlling power tools or industrial machinery.
For instance, a worker operating a machine in a factory may use a latching foot switch to keep the machine running without the need to hold down the pedal continuously.
3. Multi-Function Foot Switches
Some foot pedal switches are designed with multiple functions, allowing users to control various devices or settings with a single pedal. These switches are particularly useful in complex systems like robotic surgeries, where the surgeon may need to control multiple pieces of equipment simultaneously.
For example, in a musical performance, a multi-function foot switch may allow a guitarist to control several effects pedals at once, changing settings for distortion, delay, and reverb with a single press.

Applications of Foot Pedal Switches Across Industries
Foot pedal switches are widely used in a variety of industries, providing both efficiency and safety. Below are some key industries that benefit from the use of foot pedal switches:
Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
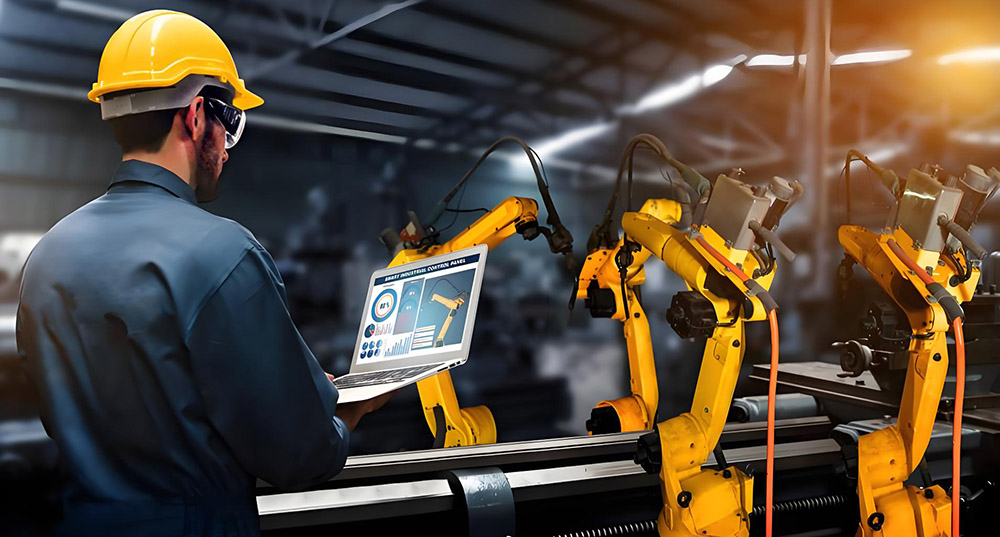

In manufacturing environments, foot pedal switches play a crucial role in streamlining operations. Operators can use foot switches to control machinery, conveyor belts, presses, and other equipment, freeing up their hands to perform other tasks. This hands-free operation allows for greater efficiency and precision in production workflows.
For example, in automotive assembly lines, foot switches allow workers to start and stop machines, adjust tools, or engage conveyor belts without needing to use their hands. This increases productivity and reduces the chances of accidents, as operators can focus on their tasks rather than constantly adjusting machinery.
Healthcare and Medical Equipment
In healthcare settings, foot pedal switches are used to operate medical devices, including surgical tools, diagnostic equipment, and hospital beds. Surgeons, dentists, and other healthcare professionals often use foot switches to control devices while keeping their hands sterile or occupied with other tasks.
For instance, during surgery, a surgeon may use a foot pedal to adjust the intensity of surgical lights, activate a suction device, or control other equipment. This allows the surgeon to remain focused on the procedure without having to manually adjust settings or equipment.
Foot switches are also commonly used in dental practices to control dental drills, water sprays, and suction devices, providing convenience and efficiency in a sterile environment.
Music and Entertainment

In the music industry, foot pedal switches are an essential tool for controlling audio equipment. Guitarists, bassists, and other musicians use foot switches to control their effects pedals, switching between different sound effects during performances. These foot switches allow musicians to adjust their tone and settings without interrupting their playing.
For example, a guitarist may use a foot pedal switch to toggle between distortion, delay, or reverb effects during a live performance, enabling them to create dynamic and evolving sounds. The convenience of foot pedal switches allows musicians to focus on their performance while having full control over their equipment.
Foot pedal switches are also used in live sound and lighting setups to control various aspects of the show. Lighting engineers, for example, may use foot switches to adjust the intensity of stage lights or trigger special effects during performances.
Robotics and Remote Operations
Foot pedal switches have also found their place in robotics and remote operations. These switches provide operators with a hands-free way to control robotic systems, making them an essential component in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
For instance, in robotic surgeries, surgeons use foot pedal switches to control robotic arms or adjust the position of surgical instruments. In industrial settings, foot switches are used to operate robotic arms, automate repetitive tasks, or control the movement of robotic systems on assembly lines.
Foot switches in robotics allow for precise control over complex machinery, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of human error.
Wiring and Setting Up Foot Pedal Switches
Proper wiring and setup are essential for the reliable performance of foot pedal switches. Whether you’re wiring a simple momentary switch or a complex multi-function pedal, here are some basic steps to follow:
Choosing the Right Foot Switch: The first step is selecting the appropriate foot switch for your application. Consider factors such as the type of switch (momentary, latching, or multi-function), the current rating, and the operating environment.
Wiring the Switch: Once you’ve selected the foot switch, you’ll need to wire it according to the circuit’s requirements. For simple momentary foot switches, this typically involves connecting the pedal’s input and output terminals to the corresponding pins on your device or machinery.
Testing the Switch: After wiring the foot switch, test it to ensure it operates correctly. Make sure the switch activates and deactivates the circuit as expected, and check for any issues such as loose connections or faulty wiring.
Securing the Switch: Once the foot switch is wired and tested, secure it to the floor or workspace to ensure it remains stable and easy to operate. Many foot switches come with mounting options to keep them in place during use.
Advantages of Foot Pedal Switches
Foot pedal switches offer several advantages, making them a popular choice across various industries:
Hands-Free Operation
Foot pedal switches allow users to operate equipment without using their hands, which increases efficiency and allows for multitasking.
Increased Safety
Many foot pedal switches come with safety features such as emergency stop functions, which can immediately halt machinery in case of an emergency, reducing the risk of accidents.
Improved Productivity
By freeing up the operator’s hands for other tasks, foot pedal switches enable smoother workflows and faster task completion, ultimately improving productivity.
Ergonomics
Foot pedal switches are designed to be ergonomically friendly, minimizing foot fatigue and providing comfortable operation over extended periods.
Conclusion
Foot pedal switches are versatile and essential tools in a wide range of industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to music and robotics. Their ability to provide hands-free control, enhance safety, and improve efficiency makes them invaluable for professionals who rely on precision and multitasking. Whether you’re a musician adjusting effects during a performance or a surgeon controlling equipment in the operating room, foot pedal switches offer a reliable solution for seamless operation.
When selecting and using foot pedal switches, consider factors such as the application, type of switch, and wiring requirements to ensure optimal performance. With the right foot pedal switch, you can enhance your control over equipment, improve productivity, and create a more efficient working environment.















